Coverage and Placement
Critter Gitter Coverage and Placement Instructions
COVERAGE
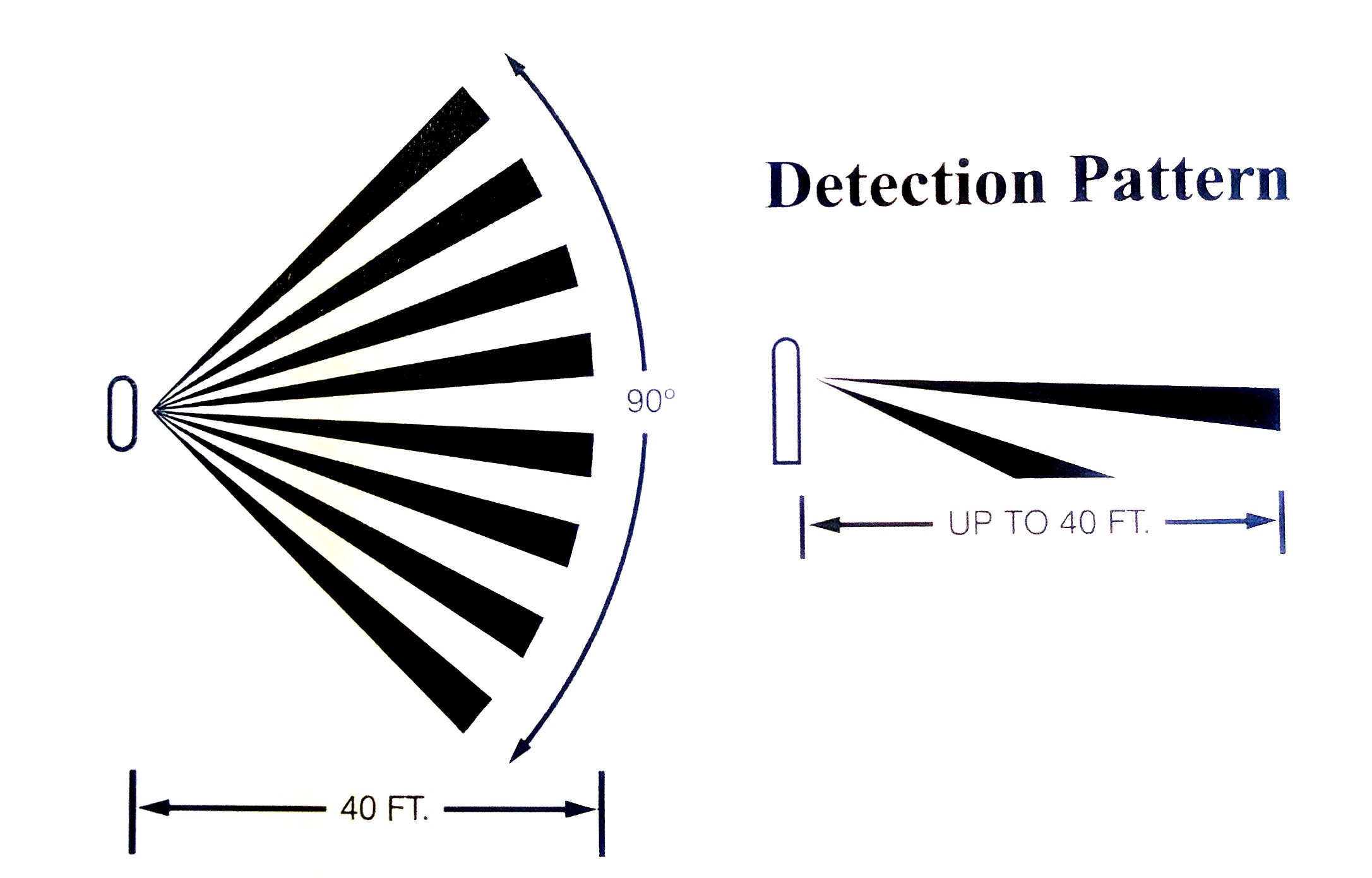
PLACEMENT
Eliminate Ambiguity
The Amtek literature recommends placing the Critter Gitter in a way that it
detects movement & infrared crossing the detection area.
KDC
recommends placing it as a deterrent to something approaching it as is
practical. From the point of view of trigger areas in the sensor,
crossing the field of view connects with more triggers but from the
point of view of minimizing ambiguity, If a bear approaches a door or
window and that door or window sounds an alarm, the animal knows not to
revisit that door or window. But, if that same animal was walking past
the protected area and the alarm sounds, the animal might not recognize
that the alarm was specifically for him or related to something it was
doing.
Here are two videos to show this point:
In this video, the bear was aware of the Critter Gitter, initially left
but later ignored it, perhaps after deciding it wasn't meant for him.
Note: Most beekeepers place the Critter Gitter on the hives and use electric fences, which when the bear does not get shocked, the Critter Gitter becomes second level protection. If the fence is in range of the Critter Gitter, the bear is "warned" and if shocked, receives double the enforcement not to return.
In this video, the deer definitely knew it was meant for him.
HOW HIGH
(Run this test yourself)
1. Start with the Critter Gitter on the ground facing an area where birds, chipmunks, squirrels, rabbits, etc. frequent.
You will find the Critter Gitter triggers on all of them.
2. Place the Critter Gitter on a bucket about 1 - 2 feet high.
You will find the Critter Gitter now only triggers on larger animals and it no longer "sees" the small ones.
Based on this test, placement optimally is at the height of what you want to detect.
To detect a small bear cub you might want it about 1 - 1 1/2 feet off the ground.
For larger animals, perhaps 3-4 feet off the ground.
If you place it above the area you want to cover pointing down, the Critter Gitter will detect both small and large animals but as in the first video, the animals might not take the alarm personally.
BIRDS
Normally, birds fly faster than the Critter Gitter can detect, but in the case of Herons, they can move too slowly for detection.
When birds are landing, hopping on the ground, or taking off, they are detectable. Some users have thought the Critter Gitter had false triggers because when they heard the sound then looked, nothing was there. Birds can be responsible for this trigger event.
STABLE MOUNTING
The Critter Gitter needs a stable mount that does no move in the wind or false triggers can occur.
(Do this test yourself)
Hold the Critter Gitter in your hand, turn it on then wave the Critter Gitter around, left and right and you will cause a trigger.



Send us your comments or questions or requests
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked